Receipt text tecognition is a text detection and text recognition project specifically built for receipts. It is composed by a mobile application (Java) and a server (Python-Flask).
These two components work together to pre-process the image and extract the text from it. Work flow:
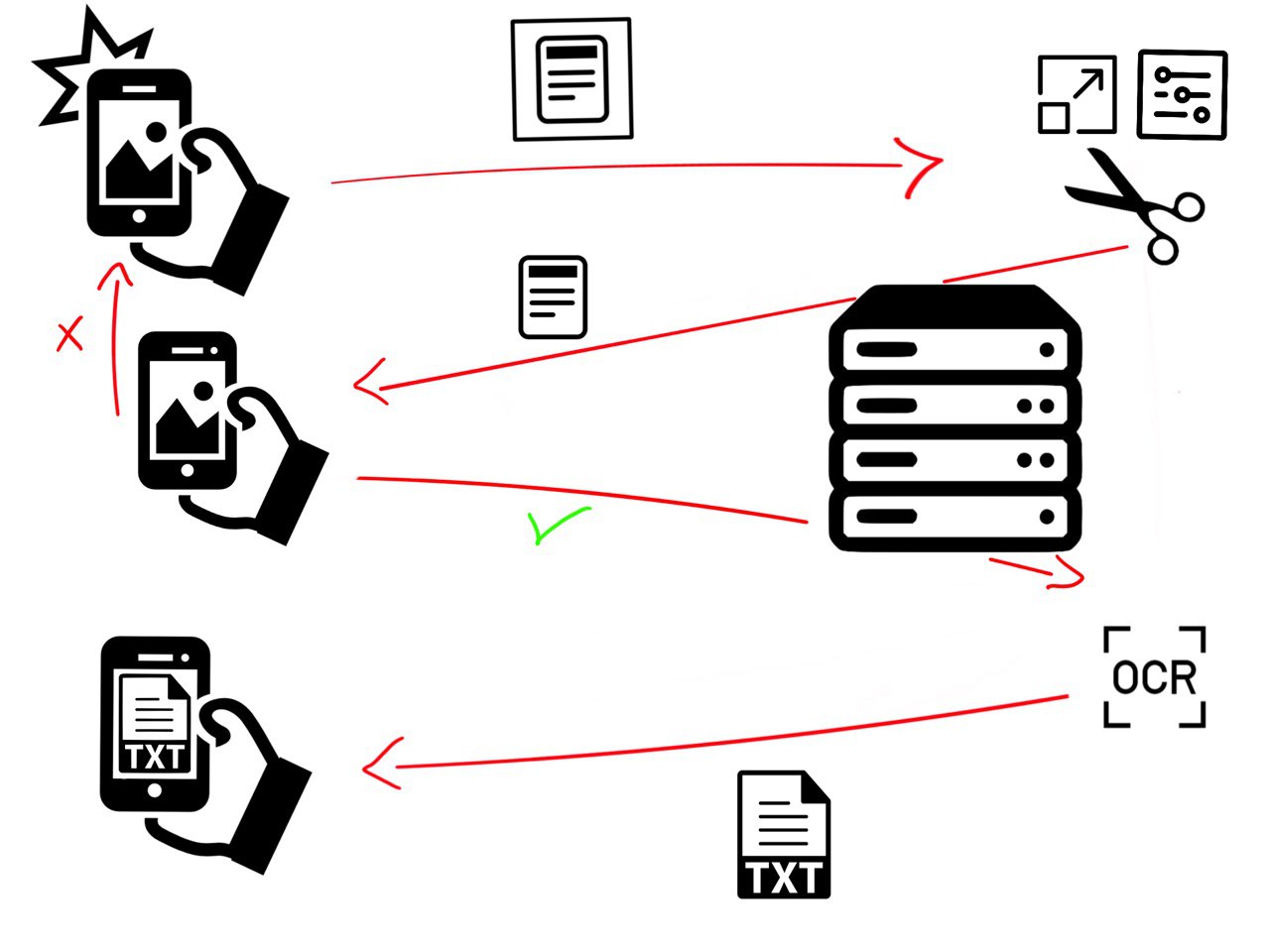
Some knowledge:
-Text detection is the process of detecting the text present in the image, followed by surrounding it with a rectangular bounding box.
-Text recognition is the process of assigning to a symbol in the image the relative alphabetical symbol.
Mobile Application
The mobile application is built for Android and it can be tested by running the code on AndroidStudio.
The goal of this application is to make the image pre-processing easier for the server by helpig the user to take the best picture possible before sending it. Otherwise the image taken could be too noisy for the server to do a good job. To do so the application implements a custom camera with some guidelines that help the costumer to take a better picture. A flash button is added to take pictures in unlit areas.
Also the application converses with the server and shows its results. In the next picture we can see the pre-processed image result received from the server.

Server
This server web is made using Flask (Python) and it is responsible for the pre-processing and text extraction.
It uses two REST API, one for binarizing and cutting the image and one that implements an OCR.
An OCR its an optical character recognition engine that transforms a two-dimensional image of text, which could contain printed or handwritten characters, from image to text representation machine readable.
For this project I used Tesseract-OCR because it is widely used for general purpose and can be setted to read structured text files, sush as receipts. Tesseract operates as follows:
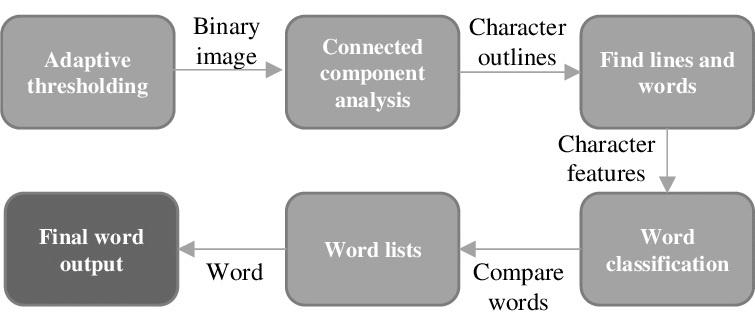
Coming to the server itself let’s analyze its APIs. The first one, as we said before, is responsible for the pre-processing and cutting. For the pre-processing the three basic operations are: grey scale image, binarization and noise removal. To do so I used two very famouse libraries: opencv and numpy. I decided to also clean the image before the binarization to reduce the number of noise after the operation, doing so the morphology open will perform better.
im_gray = Image.open(path_image_tiff).convert('L')
im_gray = np.array(im_gray)
denoise_image_1 = denoise_gaussian(im_gray)
th_image = otsu_thresholding(denoise_image_1)[1]
denoise_image_2 = denoise_morph_open(th_image)
You may notice inside ‘Image.open()’ a ‘path_image_tiff’, and you may ask yourself what does tiff means? Well tiff is an image file extension and it is a uncompressed format, that means it doesn’t loose image quality when image operations are made, also it allows us to increase the overall quality of the image by increasing the dpi attribute (Dots per Inch).
Okay! After we pre-processed the image we can crop it. For this particular task I came up with an algorithm that cuts the excess white part around the image going from this:

to this:
After this step is completed the server send the result to the client that needs to accept the image. If it does accept then the server can proceed to the text extraction with Tesseract. It seems like a long procedure but actually it is not…using Tesseract it will take only a line in Python:
dictionary = pytesseract.image_to_data(im, output_type=Output.DICT, lang="ita", config="--psm 6")
Infact ‘image_to_data’ is a pytesseract (python wrapper for Tesseract) built in method that allows us to use the power of the OCR using just one line of code. Also we can set some attributes for Tesseract to know what it is going to work with. The attribute ,output_type, tells tesseract how to output the results, in this case we are telling the OCR we want it to be a dictionary.Attribute ‘lang’ specify the text language inside the image, and last, ‘config’ tells Tesseract to treat the image as a uniform block of text. Why a uniform block of text? Well the answare is really simple: in our case a receipt has long white spaces between a product and its cost, so if we don’t tell Tesseract to treat that space as part of the line, it will think that the product name and its cost are not related and will read two different lines instead of one, making more complicated the text analisy.
The Tesseract output is now inside the dictionary, but last we need to format the text because the words are stored inside the ‘text’ key and the row to which they belong is stored in ‘line_num’, so we need to iterate throw the dictionary and create our text:
n_boxes = len(dictionary['text'])
string = ''
content = ''
current_line = -1
for i in range(n_boxes):
if int(dictionary['conf'][i]) > 0:
if dictionary['line_num'][i] != current_line:
current_line = dictionary['line_num'][i]
content = content + string + "\n"
string = ''
string = "{} {}".format(string, dictionary['text'][i])
string = content
Now the text is ready to be sent to the client.
Conclusions
If you are interested in image pre-processing and Tesseract go check my experiments on Google Colab by clicking here.
If you want to try the project just clone it from my GitHub repository here.